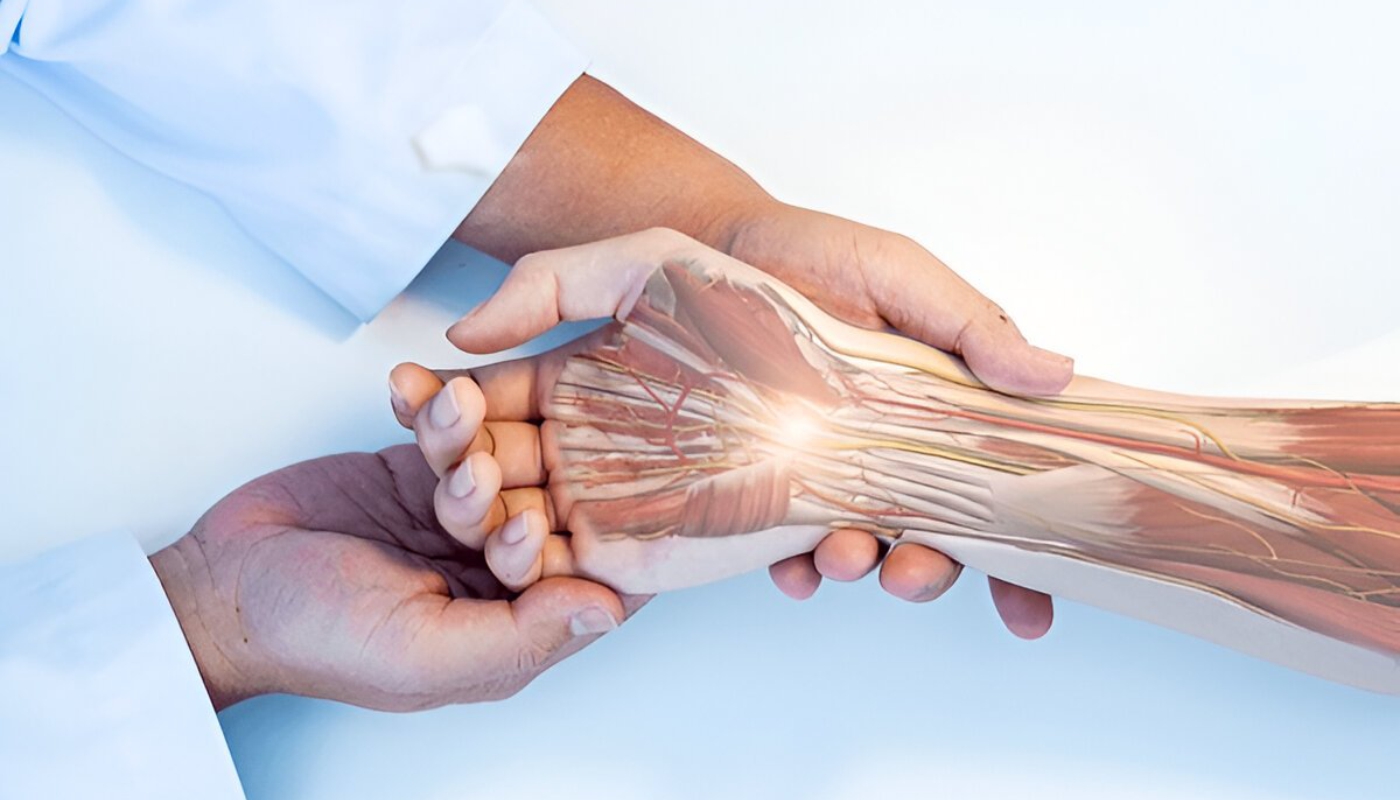
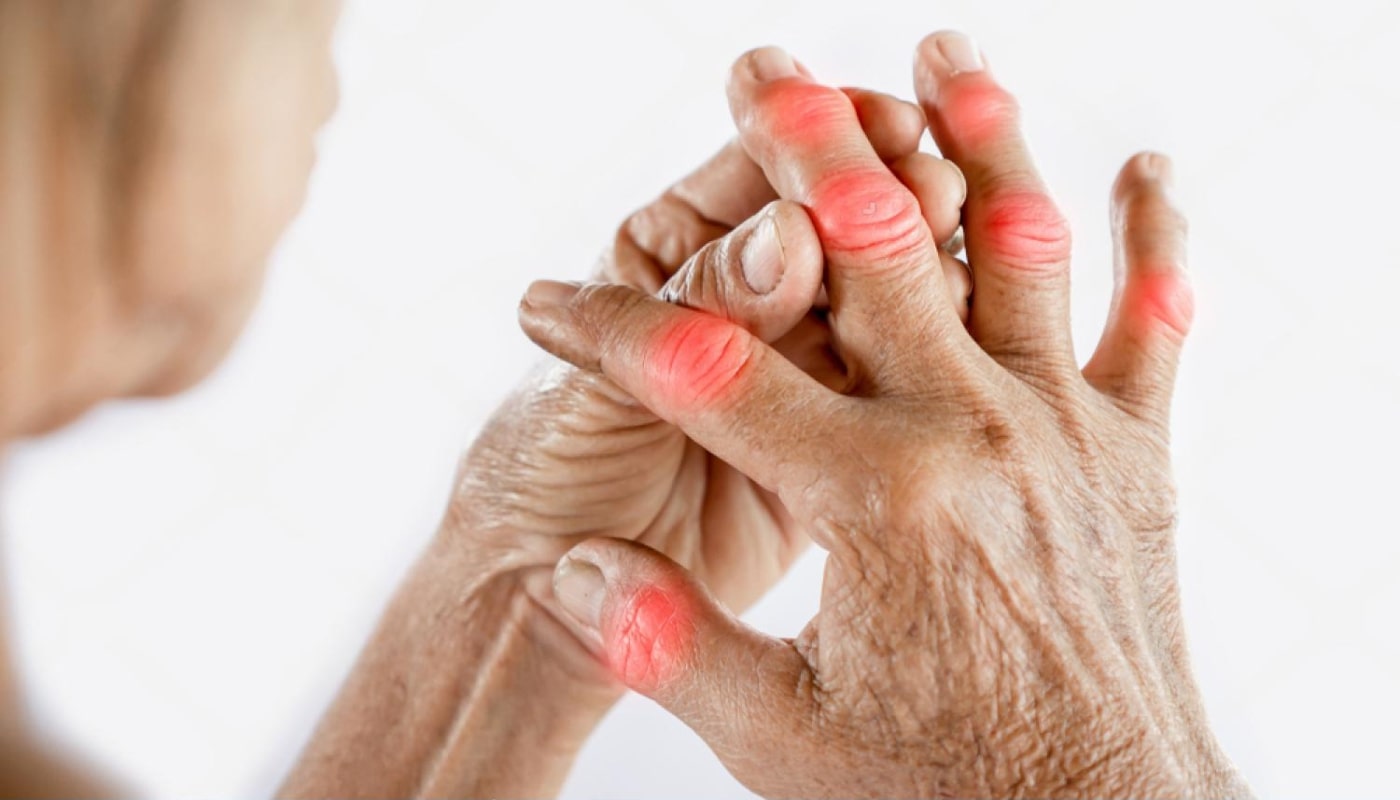
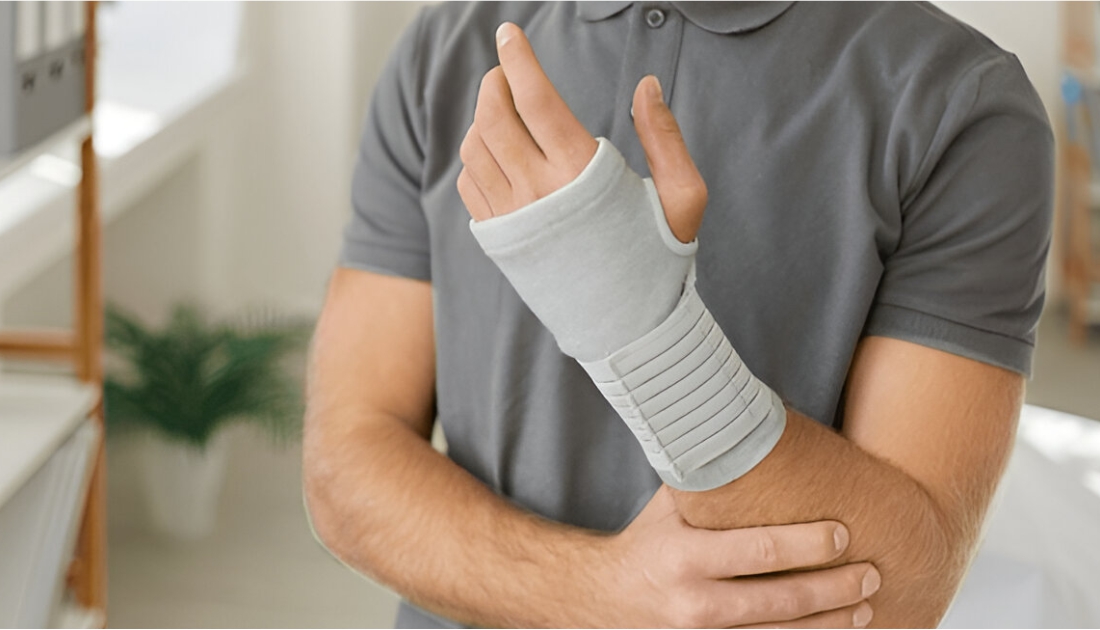
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic inflammatory disorder that primarily affects the joints, leading to pain, swelling, and eventual joint damage. Unlike osteoarthritis, which is mainly a result of wear and tear, rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease, meaning the body's immune system mistakenly attacks its own tissues. This condition can significantly impact a person's quality of life, affecting not just physical health but also emotional well-being.
Individuals with RA often experience a range of symptoms, which may include:
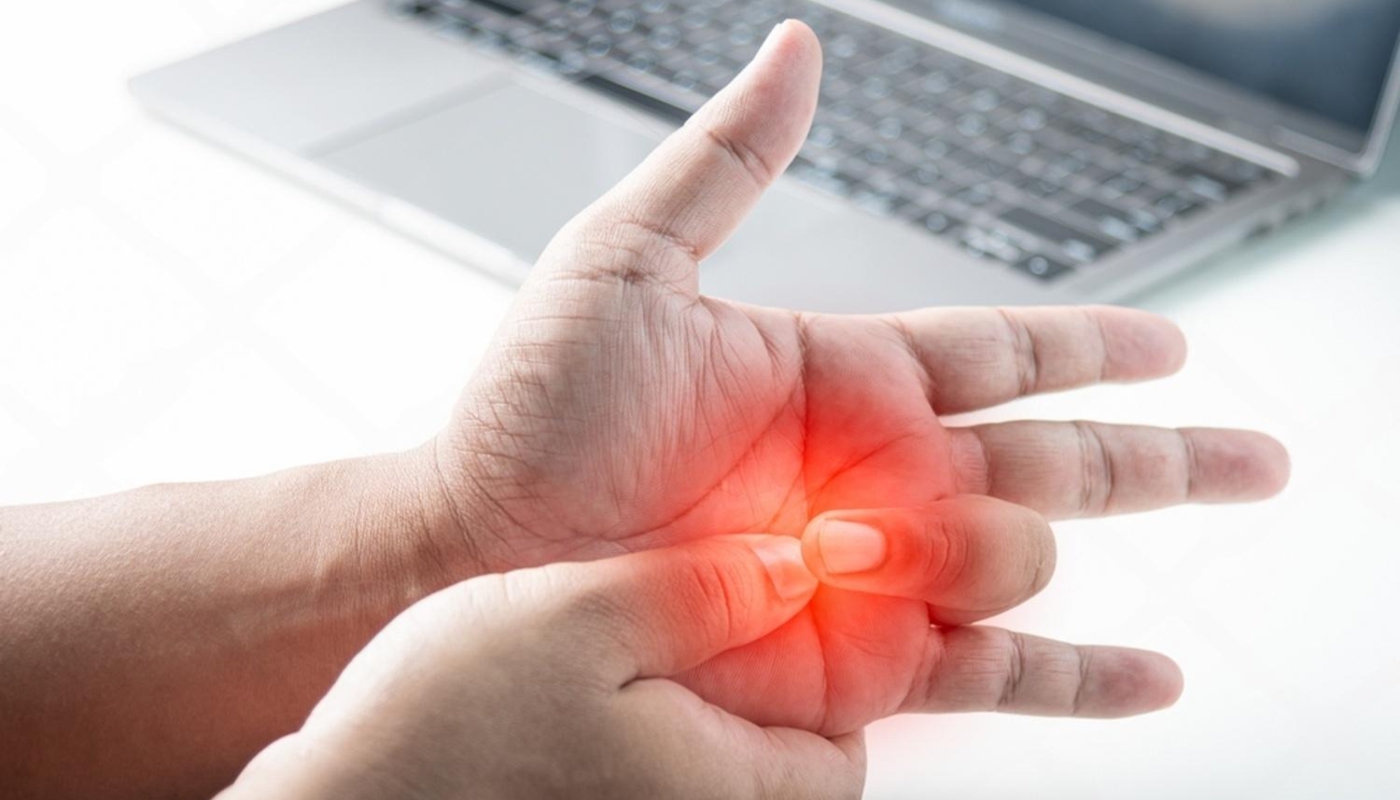
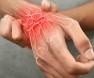
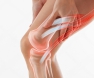
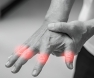
- Pain and swelling: Joints, especially in the hands and feet, can become painful and swollen due to inflammation.
- Stiffness: Many people report increased stiffness in the morning, making mobility challenging.
- Fatigue: Chronic fatigue is a common complaint, as the body is constantly fighting inflammation.
- Fever and loss of appetite: Some may experience systemic symptoms like low-grade fevers or a general feeling of being unwell.
RA can also lead to complications beyond the joints, including cardiovascular issues, lung disease, and osteoporosis. As a result, early diagnosis and appropriate management are crucial for minimizing long-term damage. Treatment options vary widely, from medications that reduce inflammation to lifestyle changes aimed at improving overall health.
At theravio.com, we provide resources and tools to help you manage rheumatoid arthritis effectively. By understanding the condition and taking proactive steps, individuals can achieve better outcomes and enhance their overall well-being.
Common Symptoms of Rheumatoid Arthritis

The symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis can vary significantly from person to person, but there are several common signs that many individuals experience. Recognizing these symptoms early can be crucial for timely diagnosis and treatment. Here are some of the most prevalent symptoms:
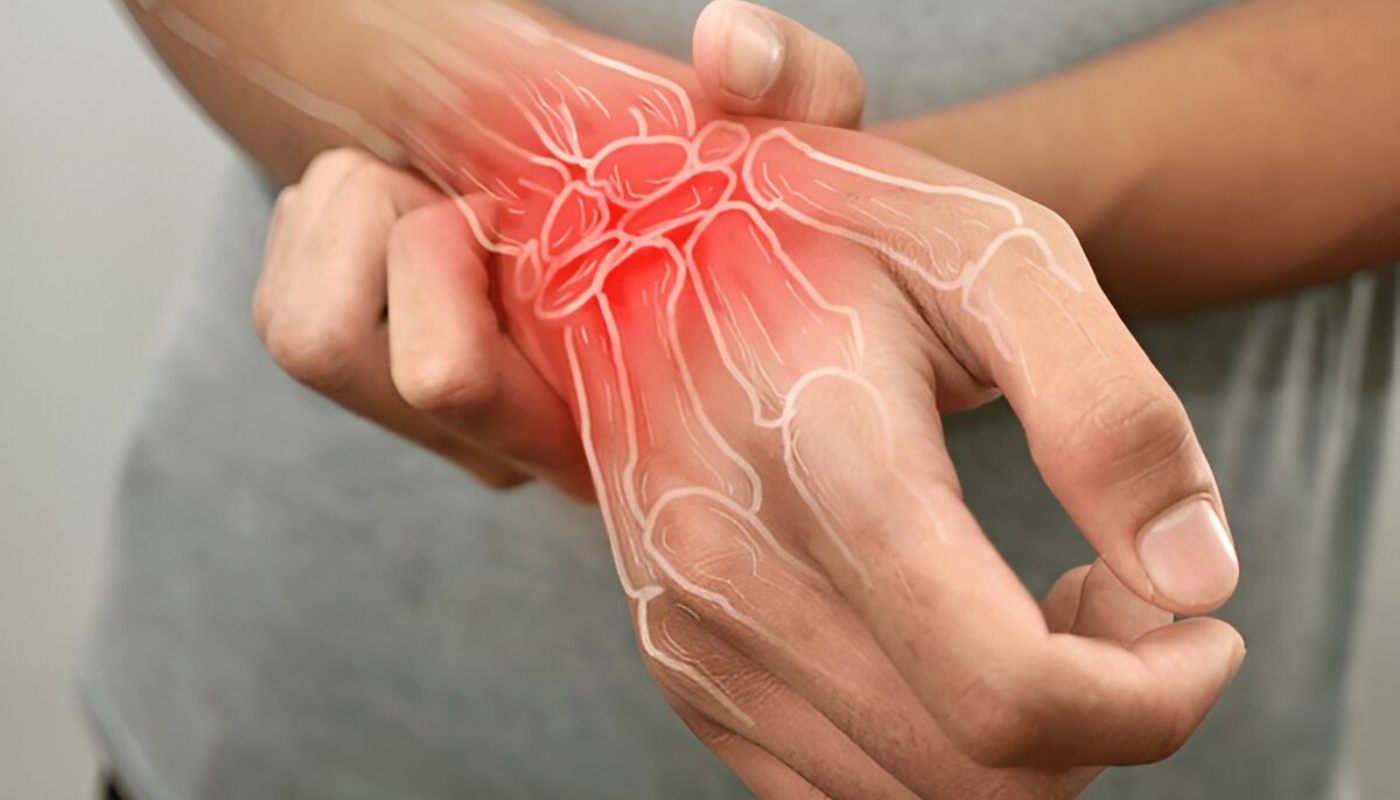
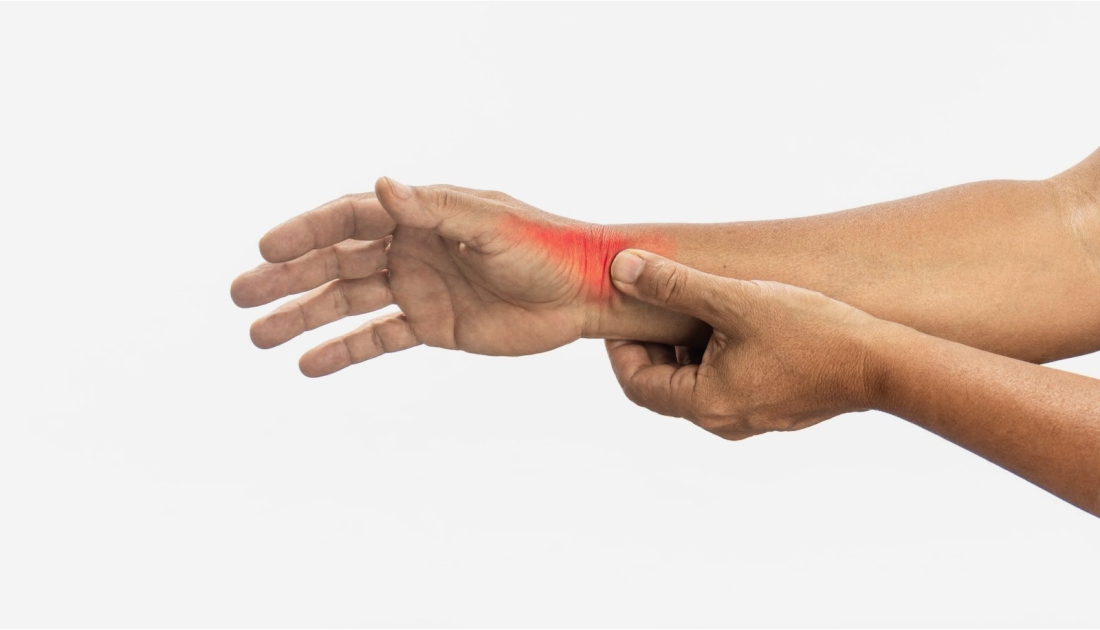
- Joint Pain and Tenderness: Individuals often report persistent pain in the joints, especially in the hands, wrists, and knees. This pain can be exacerbated by movement.
- Swelling: Inflammation can lead to noticeable swelling around the affected joints. This swelling may be accompanied by warmth and redness.
- Morning Stiffness: Many people with RA experience stiffness in their joints upon waking, which can last for over an hour. This stiffness can improve with movement throughout the day.
- Fatigue: Chronic fatigue is a common symptom, making it difficult for individuals to carry out daily activities.
- Fever and Loss of Appetite: Some may experience a low-grade fever and a decrease in appetite due to the inflammatory process.
- Joint Deformities: Over time, untreated RA can lead to joint damage and deformities, altering the structure of the hands and feet.
In addition to these physical symptoms, patients may also experience emotional challenges, such as depression and anxiety, due to the chronic nature of the disease and its impact on daily life. Understanding these symptoms is vital for seeking appropriate medical advice and finding effective treatment strategies.

Causes and Risk Factors for Rheumatoid Arthritis
Understanding the causes and risk factors for rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is essential for both prevention and management of the condition. While the exact cause of RA remains unclear, research suggests that a combination of genetic, environmental, and hormonal factors may contribute to its development.
- Genetic Predisposition: Studies show that individuals with a family history of RA are at a higher risk of developing the condition. Certain genetic markers, such as the HLA-DR4 allele, have been associated with increased susceptibility.
- Environmental Triggers: Exposure to certain environmental factors, such as smoking, can significantly increase the risk of RA. Additionally, infections may trigger the onset of the disease in genetically predisposed individuals.
- Hormonal Factors: RA is more prevalent in women than men, particularly during childbearing years. This suggests that hormonal changes may play a role in the disease's development.
- Age: The risk of developing RA increases with age, with the majority of cases occurring between the ages of 30 and 60.
- Obesity: Excess weight can contribute to inflammation and may increase the risk of developing RA, as it puts additional strain on the joints.
It is important to note that while these factors can increase the likelihood of developing rheumatoid arthritis, they do not guarantee its onset. Individuals with risk factors should remain vigilant about their health and consult healthcare professionals for preventive measures and early intervention strategies.
Diagnosis Process for Rheumatoid Arthritis
The diagnosis process for rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a critical step towards effective management and treatment. Early diagnosis can help prevent irreversible joint damage and improve the overall quality of life for patients. The process typically involves a combination of medical history evaluation, physical examinations, and advanced testing.
- Medical History: The healthcare provider will begin by taking a comprehensive medical history, including a detailed account of symptoms, family history of RA or other autoimmune diseases, and any previous medical conditions that may be relevant.
- Physical Examination: A thorough physical exam helps assess joint swelling, tenderness, and range of motion. The doctor will look for common signs of RA, such as symmetrical joint involvement.
- Laboratory Tests: Blood tests are crucial in the diagnosis of RA. Key markers include:
- Rheumatoid Factor (RF): A positive RF test indicates the presence of antibodies that are often found in RA patients.
- Anti-Citrullinated Protein Antibody (ACPA): This test is highly specific for RA and can help confirm the diagnosis.
- Inflammatory Markers: Tests like ESR (Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate) and CRP (C-reactive Protein) measure inflammation levels in the body.
- Imaging Tests: X-rays, ultrasounds, or MRI scans may be utilized to assess joint damage and inflammation. These imaging techniques can reveal changes in bones and cartilage that are indicative of RA.
Once a diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis is confirmed, healthcare providers can tailor a treatment plan that best suits the individual’s needs, optimizing their path to recovery and improved physical function.
Effective Treatment Options for Rheumatoid Arthritis
When it comes to managing rheumatoid arthritis (RA), a multifaceted approach is essential for achieving optimal results. The treatment options aim to relieve symptoms, prevent joint damage, and improve overall quality of life. Here are some of the most effective treatment strategies:
- Medications: The cornerstone of RA management, medications can be categorized as follows:
- Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): These help reduce pain and inflammation but do not slow disease progression.
- Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs (DMARDs): Medications like methotrexate are crucial for slowing the disease's progression and preventing joint damage.
- Biologics: Targeting specific components of the immune system, biologics can provide significant relief for patients who do not respond to traditional DMARDs.
- Corticosteroids: These are used for quick relief from inflammation and can be utilized in acute flare-ups.
- Physical Therapy: Engaging in tailored physical therapy can enhance mobility, strengthen muscles around joints, and improve overall function. Therapists may employ various techniques, including stretching, strengthening exercises, and manual therapy.
- Occupational Therapy: An occupational therapist can assist patients in adapting their daily activities to minimize joint strain. This includes recommending assistive devices and ergonomic tools.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Adopting a healthy lifestyle can greatly impact the management of RA. This includes a balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods, regular exercise, and stress management techniques such as yoga or meditation.
- Surgery: In severe cases where joint damage is extensive, surgical options such as joint replacement or synovectomy may be considered to restore function and alleviate pain.
Combining these treatment options allows for a personalized approach that addresses the unique needs of each individual, paving the way for a more fulfilling life despite the challenges of rheumatoid arthritis.
Lifestyle Changes to Manage Rheumatoid Arthritis
Managing rheumatoid arthritis effectively often requires more than just medications and therapies; lifestyle changes play a crucial role in enhancing well-being and minimizing flare-ups. Here are some practical adjustments that can make a significant difference:
- Balanced Diet: Incorporating anti-inflammatory foods such as fatty fish, nuts, fruits, and vegetables into your diet can help reduce inflammation. It's essential to avoid processed foods and sugars, which may exacerbate symptoms.
- Regular Exercise: Staying active is vital. Low-impact exercises like swimming, walking, and cycling can improve joint function and reduce stiffness. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity per week.
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight can alleviate excess pressure on joints, especially weight-bearing ones. A diet combined with regular exercise can help achieve and sustain a healthy weight.
- Stress Management: Chronic stress can worsen symptoms. Incorporating relaxation techniques such as yoga, meditation, or deep-breathing exercises can help manage stress levels effectively.
- Proper Sleep: Quality sleep is essential in managing pain and inflammation. Establishing a regular sleep routine and creating a comfortable sleep environment can improve sleep quality.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water is crucial for overall health and can help reduce inflammation.
Implementing these lifestyle changes can significantly enhance your quality of life and help you manage rheumatoid arthritis more effectively. For more resources and tools to support your journey to better health, visit theravio.com.